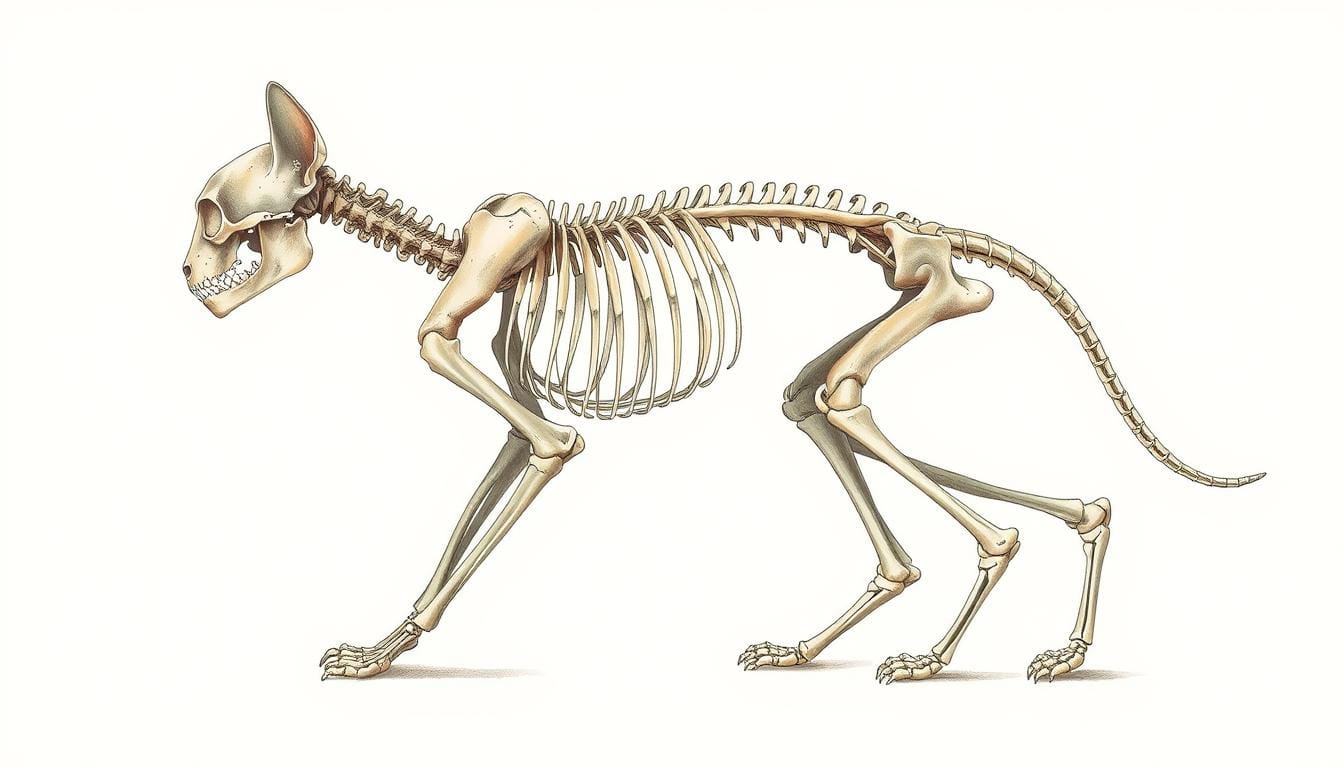
Cat Skeleton: Explore the Fascinating Anatomy of a cat’s body
Did you know cats have 230 bones, while humans have 206? This difference is why cats are so flexible and agile. They have three main skeletons: appendicular, axial, and splanchnic. These skeletons work together to help cats move and absorb shocks.
Table of Contents
Learning about cat anatomy is key to understanding their amazing abilities. Their bones, muscles, and joints allow them to jump, climb, and run with ease. As you explore their skeleton, you’ll see how their bodies are designed for agility and precision.
Key Takeaways
- Cats have 230 bones in their bodies, compared to 206 bones in humans.
- The cat skeleton is composed of appendicular, axial, and splanchnic skeletons.
- Feline anatomy is designed for flexibility, agility, and precision.
- Cats have specialized bones, muscles, and joints that enable them to jump, climb, and run with ease.
- Understanding cat skeleton and feline anatomy is essential for appreciating the remarkable abilities of cats.
- Cats rely on their flexible skeletal structure to squeeze through tight spaces and demonstrate remarkable agility.
Understanding the Basics of Feline Skeletal Structure
Exploring the world of cats reveals the importance of their skeletal structure. Their skeleton has about 250 bones, including ribs, tail bone, vertebrae, and spine. This cat bone structure makes them flexible and agile, allowing them to twist and turn easily.
The cats skeleton is split into three main parts: appendicular (limb bones), axial (skull, spine, ribs, and sternum), and splanchnic (unattached bone in soft organs). This setup helps them move freely and supports their body. Key features of their skeletal system include:
- 30 vertebrae, which help them be flexible and land on their feet
- No collarbone, letting them squeeze through tight spots
- Claws that don’t fully retract, staying partially extended
Knowing about the feline skeletal structure helps us appreciate their unique traits. It shows how their cats skeleton affects their health and well-being. By understanding the cat bone structure, we can admire the amazing framework that supports our feline friends.
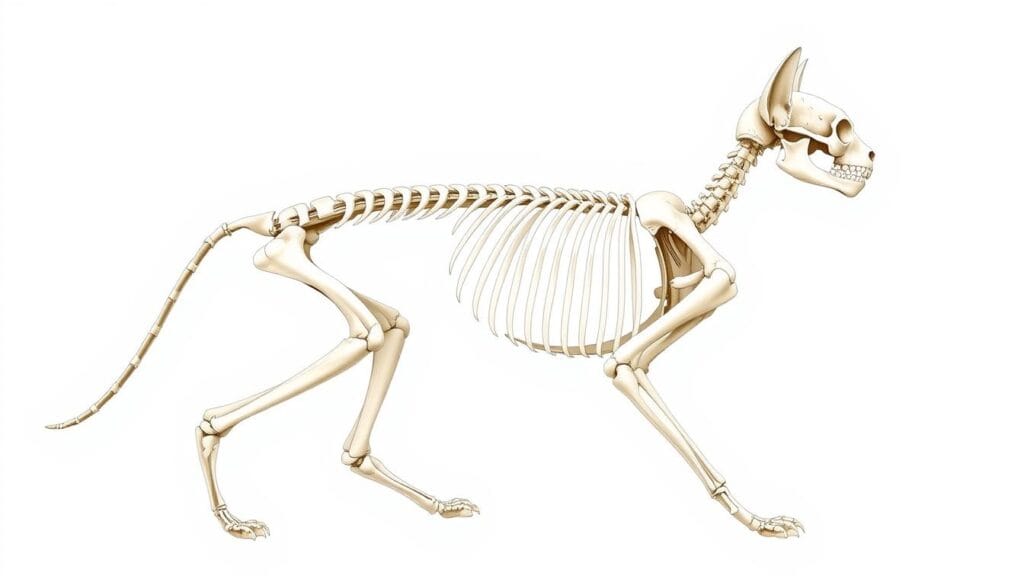

The Amazing Adaptations of a Cat Skeleton
The cat bone structure has many special features. One key feature is the lack of a collarbone. This lets cats fit into very small spaces. They also have elastic discs between their vertebrae. These discs help absorb shock and make their bones more flexible.
Some interesting facts about the cat skeleton include:
- The cat skeleton has about 250 bones.
- Most of their bones are made of cortical bone, which supports their weight.
- They also have cancellous bone, which adds strength.
The cat bone structure evolved over time. Modern cats have skulls that vary in size. Their bones are designed for a strong, precise bite. This is important for catching prey.
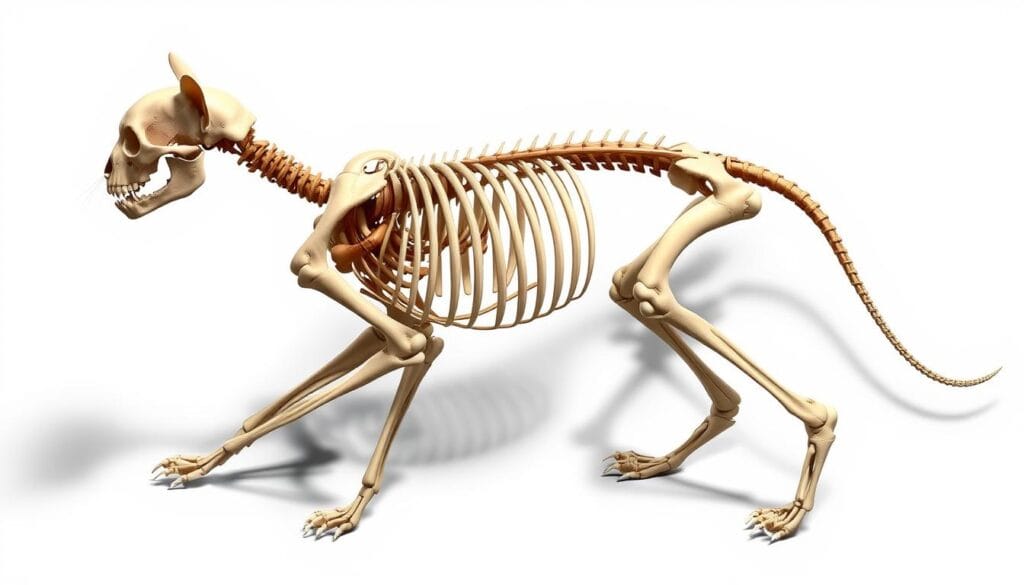
Learning about a cat’s skeleton shows us how amazing they are. By studying their bones, we can understand their evolution and development.
The Skull and Dental Structure of Cats
Looking at a cat skeleton diagram shows how their skull and teeth are made for hunting. Their skull is short and wide. This shape fits powerful jaw muscles and sharp teeth well.
Cats have 30 adult teeth for grinding and cutting food. The largest teeth, called carnassial teeth, are key for their diet. Kittens start getting 26 deciduous teeth at 3-4 weeks old.
Understanding cat bones helps us see how complex their anatomy is. By studying the cat skeleton diagram, we learn about their unique skull and teeth. These features are important for their health and well-being.
- 12 incisors, each with a singular root
- Feline canines, which are the longest teeth and also possess a singular root
- A unique jaw movement that only allows for up-and-down motion, unlike humans who have lateral jaw movement
Learning about cat bones and their functions deepens our appreciation for their anatomy. It shows how their unique features support their health and well-being.
Vertebral Column: The Foundation of Feline Flexibility
Exploring feline anatomy reveals the vertebral column’s key role. It’s essential for a cat’s flexibility and agility. The cat’s spine has 30 vertebrae, including cervical, thoracic, lumbar, caudal, and sacral vertebrae. This setup lets cats twist and turn, making them great hunters.
The cat skeleton is built for flexibility. Each vertebra is important for movement. For example, cervical vertebrae allow neck movement, while lumbar vertebrae support the lower back. This combination gives cats their flexibility, fitting them well to their surroundings.
Some key features of a cat’s vertebral column include:
- A flexible spine that allows for twisting and turning
- A unique arrangement of vertebrae that provides support and stability
- A high degree of mobility in the neck and lower back
Learning about feline anatomy and cat skeleton helps us understand cats better. By studying their spine and flexibility, we appreciate their adaptability. This adaptability lets them thrive in many environments.
Rib Cage and Chest Structure
Exploring the world of cats skeleton reveals the rib cage’s role in protecting vital organs. It also helps with breathing. The cat’s bone structure is designed for efficient breathing, thanks to a flexible diaphragm.
The rib cage, with 13 pairs of ribs, guards the heart, lungs, and other vital organs. This setup allows cats to move with ease and grace. It also keeps their internal organs safe during physical activities.
- 13 pairs of ribs that articulate with the sternebrae through cartilaginous extensions
- A diaphragm that allows for a wide range of motion, facilitating efficient breathing
- A chest structure that provides a protective enclosure for the internal organs
Learning about the cat bone structure shows the amazing design of your feline friend’s body. Knowing about the rib cage and chest helps you care for your cat’s health. This ensures they stay happy and active for many years.
Front Limb Anatomy of Your Cat
Exploring cat anatomy reveals their front limbs are special. They are made for flexibility and agility. This lets your cat move easily and precisely.
The front limbs are key for your cat’s mobility and balance. They are designed for flexibility and agility. This allows your cat to climb, jump, and pounce with ease.
Shoulder Structure
The shoulder of your cat has several important bones. These include the scapula, humerus, and radius. Together, they allow for a wide range of motion.
This makes it easy for your cat to move its front limbs. The bones are lightweight and flexible. This is perfect for agile movements.
Elbow and Wrist Joints
The elbow and wrist joints of your cat are flexible and precise. The bones and muscles in these joints allow for a wide range of motion. This lets your cat climb, jump, and pounce with ease.
The bones work together seamlessly. This provides smooth and efficient movement.
Paw Anatomy
The paws of your cat are also part of its front limb structure. They are made of small bones like the phalanges and metacarpals. These bones help with traction and support.
This allows your cat to move with ease and precision. The paw anatomy is flexible and agile. It’s perfect for climbing, jumping, and pouncing.
Hind Leg Structure and Function
The cat skeleton diagram shows how the hind leg is built for power and agility. The special way cats bones are arranged in the hind leg helps them jump and climb. The hind leg includes the femur, patella, and tibia, with strong muscles for moving and controlling.
The feline hindlimb has seven degrees of freedom. This means three at the hip and two at both the knee and ankle. This setup lets cats move in many ways, making them agile and flexible. Studying cats bones in the hind leg helps us understand how felines evolved.
The muscle paths in the hind leg are also important. Researchers found paths for 32 major muscles in the feline hindlimb. This shows that the muscle structure is very consistent across different cat species. Knowing about the cat skeleton diagram and cats bones helps us see why cats are so agile and flexible.
In summary, the hind leg of cats is a great example of evolutionary adaptation. The special bone and muscle setup lets cats jump, climb, and move with ease. By looking at the cat skeleton diagram, we can better understand the complex anatomy of cats and their amazing abilities.
The Role of Joints in Cat Movement
Exploring feline anatomy reveals the vital role of joints in cat movement. Cats have about 40 more bones than humans, making them more flexible and agile. Their bones and muscles work together in joints, allowing for jumping, climbing, and pouncing.
Cats have different types of joints, including synovial, fibrous, and cartilaginous. Each type allows for various degrees of movement. Synovial joints, like the ball-and-socket joint, offer the most freedom. Fibrous joints, on the other hand, allow little to no movement.
Cats can move their joints in many ways, thanks to their unique structure. For example, their shoulder joints are very flexible. This flexibility helps them twist and turn easily. It’s a key part of their anatomy, making them agile and precise.
Some interesting facts about feline joints include:
- Cats have various joints for different movements.
- About 75% of a cat’s skeleton is supported by ligaments.
- There are three main types of joints in cats: synovial, fibrous, and cartilaginous.
Understanding joints in cat movement shows the complex beauty of feline anatomy. Whether you’re a cat owner or enthusiast, knowing about joints helps you care for your cat better. It also lets you appreciate their special abilities.
Common Skeletal Issues in Cats
As a cat owner, knowing about common skeletal issues is key. Cats can face problems like age-related bone issues and injuries. Their bone structure is complex, so understanding it helps in caring for your cat.
Issues like osteoarthritis can cause pain and stiffness in joints. Injuries like fractures, sprains, and strains can also occur. It’s important to watch for signs like limping or trouble moving.
Other problems include developmental bone disorders, which can be genetic or caused by diet. Cats may also have osteochondromatosis, where bony growths form on bones and ribs.
To keep your cat healthy, feed them a balanced diet and ensure they exercise regularly. Monitor their weight and provide a comfy home. If you see signs of skeletal issues, get vet help. By knowing about these problems and taking action, you can help your cat stay happy and healthy.
Maintaining Your Cat’s Skeletal Health
To keep your cat’s bones strong, give them a balanced diet. Cats need lots of protein, about 70-80% of their daily calories. A good diet with calcium and phosphorus helps their bones stay healthy.
Exercise is key for your cat’s bones. Play with them or let them climb. This keeps them flexible and agile. Also, regular vet visits can catch bone problems early.
Here are some important tips for your cat’s bone health:
- Give them a balanced diet that fits their needs
- Make sure they get enough exercise
- Take them to the vet regularly
By following these tips, you can keep your cat happy and healthy. Always talk to your vet for advice on your cat’s bone health.
Growth and Development of Cat Bones
As a cat owner, you might wonder about your cat’s bone growth. This process starts in the womb and goes on until they’re adults. Knowing about kitten bone development helps you care for your cat better. Cats have three main skeletons: appendicular, axial, and splanchnic, which form their skeletal system.
The growth of cat bones is quite complex. Research shows that growth plates at joints start closing around 4-5 months. Cats usually reach full size between 12-18 months. Female cats stop growing by 10-12 months, while males might grow until 18 months or more.
Kitten Bone Development Stages
Kitten bone development includes the formation of their skeletal system. This system has three main parts: appendicular, axial, and splanchnic skeletons. A cat skeleton diagram can show these parts clearly. Regular vet visits are key during this time to catch any bone issues early.
Adult Bone Maintenance
Keeping adult bones healthy is vital for your cat’s well-being. A balanced diet and regular exercise are key. As your cat ages, watch their bone health closely and adjust their care as needed. Understanding cat bone growth helps you care for your cat and ensure they live a long, healthy life.
Conclusion: Understanding Your Cat’s Remarkable Framework
Exploring your cat’s skeletal system reveals amazing adaptations. These help them move with grace and strength. Knowing about their anatomy and skeleton is key to caring for them well.
Cats have a unique body plan, with more vertebrae and special senses like whiskers. These features make them great hunters. Understanding these traits helps you meet your cat’s needs, keeping them healthy and happy.
Regular vet visits, a good diet, and exercise are vital for your cat’s bones. With this knowledge, you can support your cat’s health. This strengthens your bond and helps them reach their full health.
FAQ
What is the total number of bones in a cat’s skeleton?
Cats have about 250 bones. This is more than the 206 bones in a human skeleton.
How does a cat’s skeletal structure differ from a human’s?
Cats have a more flexible spine and no collarbone. Their bones and muscles in the limbs are arranged differently. This allows for greater flexibility and agility.
What are the main adaptations of a cat’s skeleton?
The cat’s skeleton is made for flexibility, agility, and precision. It lacks a collarbone and has elastic discs between vertebrae. The joints are also unique.
How is the cat’s skull and dental structure adapted for hunting and eating prey?
The cat’s skull is short and wide. It has powerful jaw muscles and sharp teeth. The jaw mechanics and movement are designed for hunting, allowing the cat to grasp and tear prey.
What is the role of the cat’s vertebral column in its flexibility?
The cat’s vertebral column, with 30 vertebrae, is key to its flexibility. It allows for a wide range of motion.
How is the cat’s rib cage and chest structure adapted?
The rib cage protects vital organs. The breathing mechanics are efficient, with a diaphragm that allows for a wide range of motion.
What adaptations are found in the cat’s front and hind limb anatomy?
The front limbs are flexible and agile. The hind legs are powerful and agile, with unique bone and muscle arrangements.
What types of joints are found in a cat’s skeleton, and how do they contribute to flexibility?
Cats have various joints, including ball-and-socket, hinge, and pivot joints. Each type allows for a wide range of motion and flexibility.
What are some common skeletal issues that can affect cats?
Common issues include age-related bone problems like osteoarthritis. Injuries like fractures, sprains, and strains can also occur.
How can you help maintain your cat’s skeletal health?
Feed a balanced diet with essential nutrients. Provide regular exercise and routine veterinary check-ups. This supports your cat’s bone health and overall well-being.
What are the key stages of kitten bone development?
Kitten bone development starts in the womb and continues until adulthood. It involves the formation of the appendicular, axial, and splanchnic skeletons.
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.